Your Step-by-Step Guide To Conducting Effective Medical Audits
Medical audits are no longer just optional paperwork; they are the foundation of modern quality improvement and revenue preservation. Healthcare businesses can identify hidden compliance issues before regulators or payers by conducting a thorough examination of paperwork, coding accuracy, and clinical procedures.
A well-planned audit also identifies challenges that annoy physicians and drive up expenses. In this blog, you’ll learn the process from selecting the appropriate audit scope to taking remedial measures, so that your next medical audit results in quantifiable, sustained improvement for patients and profitability.
What is a Medical Audit?
A medical audit is a controlled assessment of clinical records, billing data, or operational processes to ensure that treatment was provided and documented by established standards.
Unlike a financial audit, which focuses on dollars and cents, a medical audit asks, Did we deliver the appropriate care at the appropriate time and document it properly?
Common lenses include:
- Clinical Quality – Are treatment decisions evidence-based?
- Coding and Billing – Do ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes correspond to the services provided?
- Regulatory Compliance – Are HIPAA, CMS, and Joint Commission requirements being followed?
Why Medical Audits Matter
Patient Safety and Outcomes
Identifying documentation gaps, such as missing allergies or medication histories, helps to reduce clinical errors and enhance continuity of treatment.
Revenue Integrity
Accurate coding decreases underpayments, rejections, and refunds following payer audits. According to CMS, each 1% movement in the incorrect payment rate results in billions of dollars in lost income for US healthcare.
Regulatory Confidence
When the Office of Inspector General or state surveyors come, a proactive audit history demonstrates good faith compliance and can result in reduced fines.
Types of Medical Audits
| Audit Type | Timing | Focus |
| Prospective | Before a claim is submitted | Prevent coding errors upfront |
| Concurrent | During the patient encounter | Ensure real-time documentation quality |
| Retrospective | After services are rendered | Review end-to-end accuracy |
| Internal | Led by in-house staff | Continuous quality improvement |
| External | Performed by third parties | Independent validation, often payer-driven |
Preparing for Audit
1. Define Goals and Scope
Begin with a clear question: What do we wish to improve? It might be a single specialty, a particular Diagnosis-Related Group, or the full revenue cycle. The narrow scope reduces audit fatigue.
2. Form a Multidisciplinary Team
- Physicians or advanced practice providers for clinical insight.
- Coding and billing professionals.
- Officers responsible for quality improvement or compliance.
- IT Support for Data Pulls
A balanced team guarantees that results are clinically and operationally sound.
3. Establish Standards and Benchmarks
Use trusted sources
- CMS Local Coverage Determinations
- Joint Commission Standards
- Specialty-society recommendations like ACR Appropriateness Criteria.
Document these standards so that any auditor may assess documents using the same criteria.
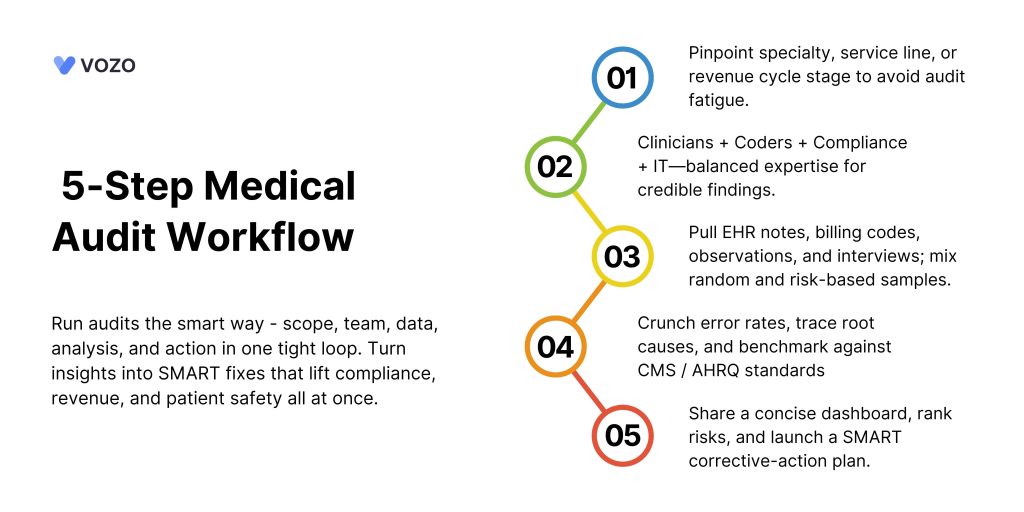
Data Collection Techniques
The audit’s success or failure depends on the collection of verifiable data. Mix approaches to get a whole picture.
- EHR Records review extracts both structured data, such as diagnoses, orders, and free-text notes.
- Coding abstracts compare billing codes and clinical documents.
- Direct observation of shadow processes to ensure that practice meets policy.
- Interviews with providers or staff help to identify knowledge gaps and real-world limits.
- Surveys and checklists standardize responses for simpler quantification.
Random sampling lowers bias. In high-risk locations, utilize intentional risk-based sampling to focus on recognized problem sites.
Analyzing Data
1. Quantitative Review
Calculate error rates, missed charges, and guideline adherence. Benchmark against:
- Historical internal data.
- National databases such as the AHRQ Quality Indicators
- Payer denial statistics
2. Qualitative Review
Read tales to discover the core reasons. Miscoded procedures may be the result of bad EHR drop-down design rather than coder incompetence.
3. Root Cause Analysis
Use “5 Whys” or fishbone diagrams to identify process problems, training shortfalls, or systemic hurdles.
Reporting Your Findings
A brief, actionable report speeds up transformation.
- Executive Summary – One page with essential metrics, trends, and urgent improvements.
- Methodology – Sampling frame, standards applied, audit period.
- Findings – Quantitative tables and qualitative narratives. Use straightforward English.
- Risk Ranking – High, medium, and low. Highlight any things that have a financial or patient-safety impact.
- Recommendations – Specific, prioritized, and related to fundamental issues.
Visual tools, such as bar charts for mistake rates and heat maps for denial hotspots, help stakeholders rapidly understand priorities.
Develop a Corrective Action Plan
A report without follow-up is only paperwork. Convert discoveries into a living CAP.
SMART Goals
- Specific – Reduce E/M down-coding by 20%.
- Measurable – Track monthly using the KPI dashboard.
- Achievable – Funded by the training budget.
- Relevant – aligns with the revenue integrity aim.
- Time-bound: Achieve within two quarters.
Ownership and Timeline – Assign each activity to a role, not a committee.
Resources – software patches, continuing medical education classes, and policy rewrites.
Monitoring Method -Define metrics and a reporting schedule.
Best Practices for Medical Audit Success
1. Automate Where Possible
Use audit tools or EHR analytics to highlight documents based on rule sets. Automation allows auditors to focus on interpretation rather than data searching.
2. Keep an Audit Trail
Document every step, criteria, samples, and communication to support choices during payer disputes or legal reviews.
3. Foster Psychological Safety
Position audits as learning opportunities rather than witch hunts. When clinicians feel secure, they disclose context, which reveals systemic weaknesses.
4. Coordinate With the Compliance Calendar
Align medical audits with other assessments (privacy, OSHA, coding) to prevent redundancy and employee burnout.
5. Stay Current with Regulations
Subscribe to get CMS transmittals and OIG Work Plan updates. Standards change, and so should your audit checklist.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
| Pitfall | Why It Hurts | How to Avoid |
| Overly Broad Scope | Dilutes focus, overwhelms staff | Start small, expand in phases |
| Inconsistent Criteria | Skews findings, erodes trust | Use a single, documented standard set |
| Poor Communication | Stakeholders ignore results | Share bite-sized dashboards, host Q&A sessions |
| No Follow-Up | Problems recur unchecked | Build CAP with clear owners and deadlines |
| Blaming Culture | Staff hide errors | Emphasize process improvement, not punishment |
Related: From Manual to Automated: Transforming Medical Billing for Faster Payments
Vozo EHR Integrated with Medical Billing
Medical billing is a complex healthcare operation that requires efficiency and precision. Delayed payments, claim denials, and manual errors can slow your revenue cycle and affect cash flow.
With Vozo’s Cloud EHR solution, you get an integrated medical billing system that simplifies your billing process and enhances real-time claim tracking to improve payment turnaround.
How Vozo EHR Transforms Medical Billing:
- Streamline billing workflows and reduce administrative workload.
- Instantly identifies and corrects coding errors before claim submission.
- Speeds up claim verification with automated payer communication.
- Ensures compliance with built-in coding checks and regulatory updates.
- Offers real-time analytics and reporting for better decision-making.
- Minimizes delays by automating claims processing and payments.
- Reduces billing disputes with accurate, transparent invoicing.
Vozo EHR’s seamless integration with medical billing empowers healthcare providers to reduce errors, prevent delays, and optimize revenue cycles, all while focusing on delivering better patient care.
About the author

With more than 4 years of experience in the dynamic healthcare technology landscape, Sid specializes in crafting compelling content on topics including EHR/EMR, patient portals, healthcare automation, remote patient monitoring, and health information exchange. His expertise lies in translating cutting-edge innovations and intricate topics into engaging narratives that resonate with diverse audiences.